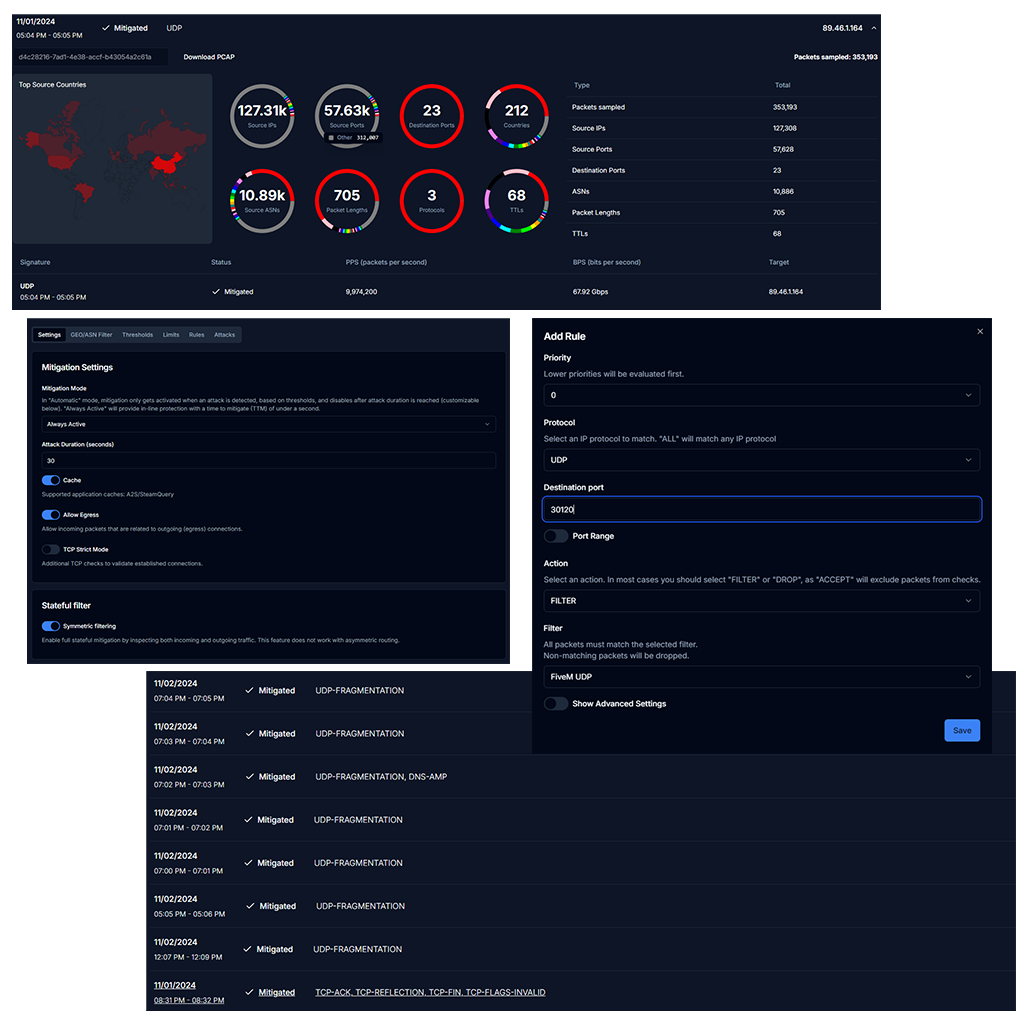
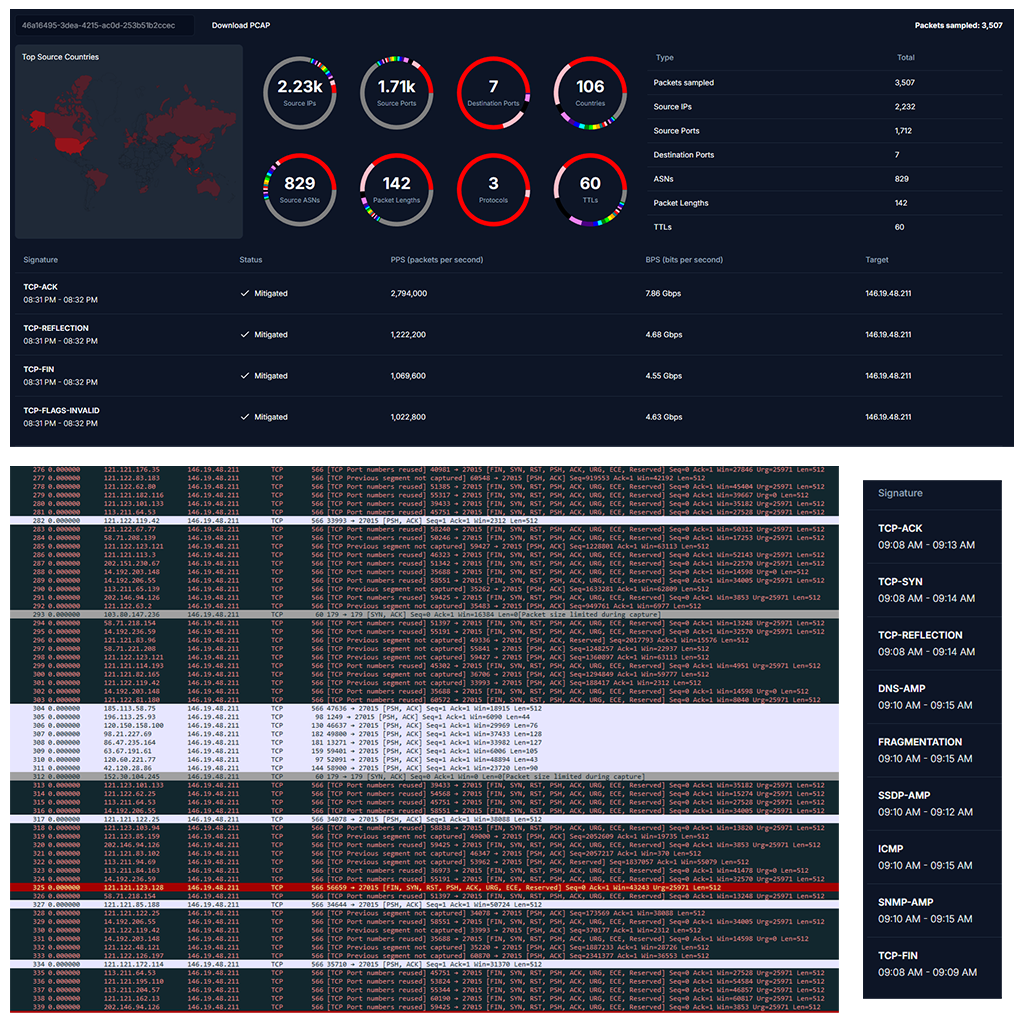
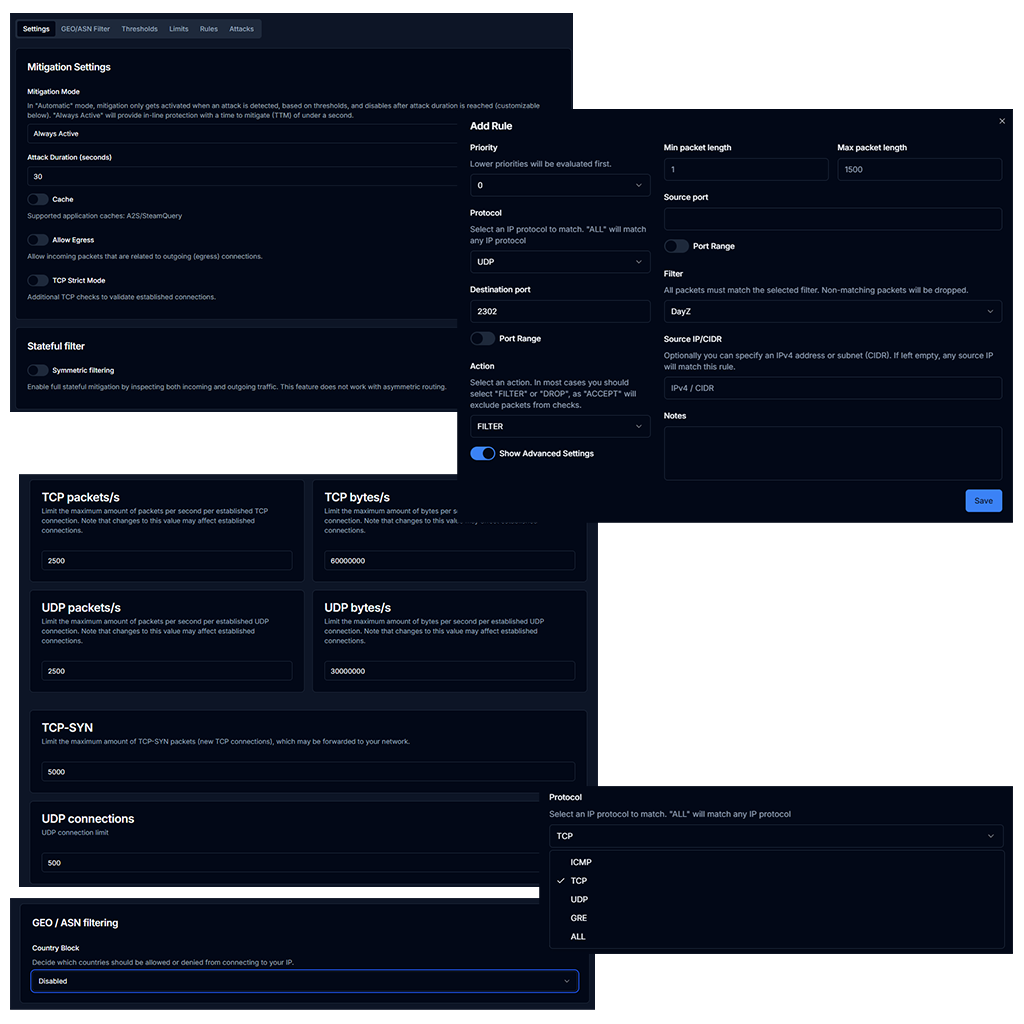
-
Hosting
- Bare-Metal Dedicated ServersGet industry-leading hardware at an affordable dedicated server price.
- Dedicated Virtual ServersJust like a VPS but the resources are Dedicated to you running on our amazing 7950x infrastructure.
- Game ServersPure dedicated performance game servers, built on our infrastructure of 7950x servers world wide.
- Infrastructure
- Company
- Support
- Login
- Register